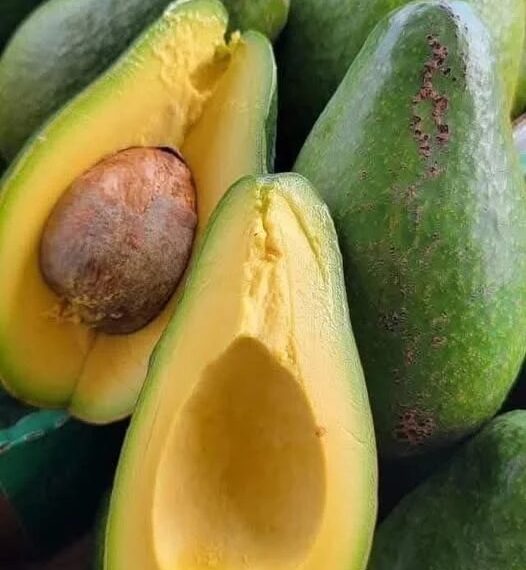
Avocados have earned a reputation as a “superfood,” celebrated for their creamy texture, rich flavor, and impressive nutritional profile. Packed with healthy fats, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, they have become a staple in diets worldwide, from smoothies and salads to toast and desserts.
But like any food, moderation is key. While avocados offer numerous health benefits, excessive consumption can lead to unwanted effects. Doctors and nutritionists are increasingly emphasizing that even the healthiest foods can pose challenges if eaten in large quantities.
The Health Benefits of Avocados
Rich in Healthy Fats
Avocados are abundant in monounsaturated fats, particularly oleic acid, a heart-healthy fatty acid. Unlike saturated fats found in red meat or butter, monounsaturated fats can help reduce bad LDL cholesterol while maintaining or increasing good HDL cholesterol. This contributes to improved cardiovascular health and reduced risk of heart disease.
Supports Heart Health
The combination of healthy fats, potassium, and antioxidants in avocados makes them excellent for heart health. Potassium helps regulate blood pressure by balancing sodium levels, reducing the strain on blood vessels and the heart. Regular avocado consumption may support a healthy cardiovascular system when included in a balanced diet.
Rich in Fiber and Vitamins
Avocados are an excellent source of dietary fiber, which promotes digestive health and satiety. Fiber helps regulate bowel movements, supports healthy gut bacteria, and may assist in weight management when consumed in appropriate portions.
They also provide important vitamins, including:
- Vitamin E: A powerful antioxidant that protects cells from oxidative stress.
- Vitamin C: Supports the immune system, skin health, and tissue repair.
- B-vitamins: Essential for energy production and neurological health.
Potassium Powerhouse
A medium avocado contains more potassium than a banana, making it an excellent choice for maintaining electrolyte balance, supporting muscle function, and protecting kidney health.
Antioxidants and Phytochemicals
Avocados are rich in carotenoids like lutein and zeaxanthin, which protect eye health. Antioxidants in the fruit combat inflammation and may help reduce the risk of chronic diseases over time.
Potential Risks of Overconsumption
Even with these impressive benefits, overindulgence in avocados can have side effects. Here are some concerns doctors highlight:
Weight Gain
While avocados are nutritious, they are also calorie-dense. A single avocado contains roughly 250–300 calories, mostly from fat. Eating multiple avocados per day without accounting for the extra calories can slow weight loss or even contribute to weight gain. Portion control is essential: a quarter to half an avocado per day is generally considered a healthy serving for most adults.
Gastrointestinal Problems
Avocados contain significant fiber, which is great for digestion—but too much fiber can lead to digestive issues in sensitive individuals. Overconsumption may result in gas, bloating, or diarrhea. People who are not accustomed to a high-fiber diet should increase avocado intake gradually to allow the gut to adapt.
Allergic Reactions
Next page